INTRODUCTION TO THE FRAMEWORKS
- hassamadhi9594
- Feb 13, 2019
- 6 min read
Updated: Feb 20, 2019
01).declarative and imperative paradigms :
Declarative paradigms is when you say what you want, and imperative paradigms is when you say how to get what you want. Declarative paradigms is a programming paradigm that expresses the logic of a computation(What do) without describing its control flow(How do).
Imperative paradigms is a programming paradigm that describes computation in terms of statements that change a program state.
As an example of declarative paradigms:
constsum= a=> b=> a + b;
print(sum(5) (3)); // 8
As an example of imperative paradigms:
add (x, y) {
return x + y;
} add(5, 9);
In imperative paradigms execution of a code block, changes the state of the system.
Class action {
n = 5; show(){
print(this.n);
} add (x) {
this.n= this.n+ y;
} }
02).Difference between procedural programming and functional programming :
In procedural programming everything is done in a specific order but in functional programming order of evaluation is usually undefined.
In procedural programming execution of a routine may have side effects but in functional programming must be stateless. i.e. No operation can have side effects.
In procedural programming, the output of a routine does not always have a direct correlation with the input but in functional programming always returns the same output for a given input.
In procedural programming tends to emphasize implementing solutions in a linear fashion but in functional programming tends to emphasize a divide and conquer approach.
03).The Lambda calculus and Lambda expressions in functional programming :
Lambda calculus is a model of computation devised in the 1930s by Alanzo Church. It’s one process for formalizing a method. Like Turing machines it formalizes the concept of effective computability, thus determining which problems or classes of problems, can be solved. Functional programming languages are based on Lambda Calculus. Imperative languages usually treat functions differently than other values(variables, objects and other inhabitants of a program) in the program though that is changing with omnipresence of lambdas(anonymous) function everywhere.
04).What is meant by “no side-effects” and “referential transparency” in functional programming?
Referential transparency are properties of parts of computer program. An expression is called referentially transparent if it can be replaced with its corresponding value without changing the program's behavior. This requires that the expression is pure, that is to say the expression value must be the same for the same inputs and its evaluation must have no side effect.
In functional programming, side effects are rarely used. The lack of side effects makes it easier to do formal verification of a program. Functional languages such as Standard ML, Scheme and Scala do not restrict side effects, but it is customary for programmers to avoid them.
05).Instantiation and Constructors :
A Constructor is a kind of Method. It has the extra feature that it creates (instantiates) new Objects.
A Method is a kind of Procedure. It has the extra rule that it must be part of a Class and/or Object.
A Procedure in OOP is the same as a Procedure in non-OOP languages.
Inheritance :
When one Class Inherits from another Class, it adopts the type of the other Class, and adopts all the Methods and Attributes. The new Class can be treated as if it is the old Class - Procedures don't need to know whether they are seeing a new Class or an old one. The original Class is usually called a superclass and the new (inheriting) Class is called a subclass.
Overriding :
When a subclass extends a superclass, it can optionally replace any of the superclass's Methods with new, customized versions. This act of replacing is Overriding, and the old version is described as overridden.. The replacement method in the subclass may (but need not) invoke the overridden method of the superclass, as well as carrying out additional operations required by the subclass.
Overloading :
Most OO languages allow redefinition of the standard arithmetic operators (+,-,*,/,...) so they can be applied to members of a class, or to a class and a standard variable type ( real number, integer,..). As with polymorphism, the appropriate method (which must be part of the class definition) may be selected at run time.
06).How the event-driven programming is different from other programming paradigms?
Focus on the events triggered outside the system
•User events (Click, drag/drop, key-press, etc.)
•Schedulers/timers
•Sensors, messages, hardware interrupts
Mostly related to the systems with GUIs, where the users can interact with the GUI elements.
Use event-listeners (event-handlers) to act when the events are triggered/fired.
An internal event loop (main loop) is used to identify the events and then call the necessary handlers.Can be seen as inversing the control to the event machine.
The event machine calls your code as the events trigger.
07). The Compiled languages, Scripting languages, and Markup languages
In compiled languages some executables can be directly run on the OS, but in Scripting languages source code is not compiled, it is directly executed and there is no execution process for the markup languages.
In compiled languages some executable use virtual runtime machines but in Scripting languages at the execution time, the code is interpreted by a runtime machine and the tools who have the knowledge to understand the markup languages can render the output.
08).The role of the virtual runtime machines
In computing, a virtual machine is an emulation of a computer system. Virtual machines are based on computer architecture and provide functionality of a physical computer. Their implementations may involve specialized hardware, software, or a combination. Current use includes virtual machines that have no direct correspondence to any real hardware. The physical, "real-world" hardware running the VM is generally referred to as the 'host', and the virtual machine emulated on that machine is generally referred to as the 'guest'. A host can emulate several guests, each of which can emulate different operating systems and hardware platforms.
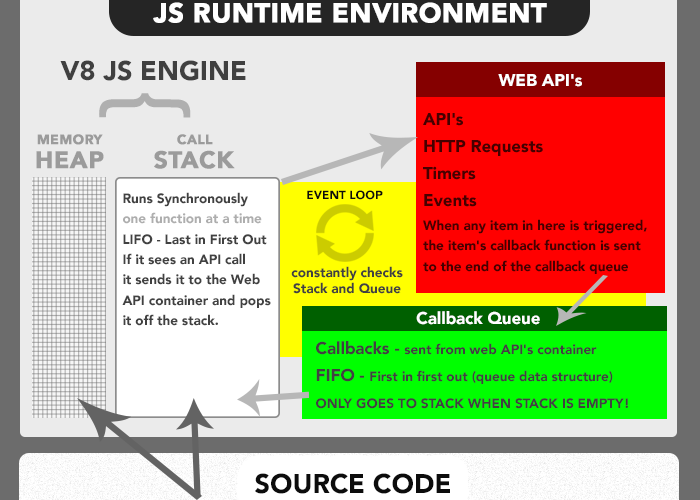
09). How the JS code is executed (What is the runtime? where do you find the interpreter?)
Think of the JS runtime environment as a big container. Within the big container are other smaller containers. As the JS engine parses the code it starts putting pieces of it into different containers. The first container in the environment is called the ‘memory heap’. The second container in the environment is called the ‘call stack’. Once a function is added to the Stack the JS engine jumps right in and starts parsing its code, adding variables to the Heap, adding new function calls to the top of the stack, or sending itself to the third container where Web API calls go. When a function returns a value, or is sent to the Web API container, it is popped off the stack and moves to the next function in the stack. If the JS Engine gets to the end of the function and no return value is explicitly written, the JS Engine returns undefined and pops off the function from the stack.
A JavaScript engine is a program or interpreter which executes JavaScript code. A JavaScript engine may be a traditional interpreter, or it may utilize just-in-time compilation to bytecode in some manner. Although there are several uses for a JavaScript engine, it is most commonly used in Web browsers.
10). How the output of an HTML document is rendered, indicating the tools used to display the output
An HTML element is an individual component of an HTML (Hypertext Markup Language) document or web page.HTML is composed of a tree of HTML nodes, such as text nodes. Each node can have HTML attributes specified. Nodes can also have content, including other nodes and text. Many HTML nodes represent semantics, or meaning. For example, the <title> node represents the title of the document.
11). Identify different types of CASE tools, Workbenches, and Environments for different types of software systems (web-based systems, mobile systems, IoT systems, etc.)
Computer Aided Software Engineering (CASE) tools are used throughout the engineering life cycle of the software systems
Requirements –Surveying tools, analyzing tools.
Designing –Modelling tools.
Development –Code editors, frameworks, libraries, plugins, compilers.
Testing –test automation tools, quality assurance tools.
Implementation –VMs, containers/dockers, servers.
Maintenance –bug trackers, analytical tools.
CASE software types
Individual tools –for specific task
Workbenches –multiple tools are combined, focusing on specific part of SDLC
Environments –combines many tools to support many activities throughout the SDLC
12). The difference between framework, library, and plugin, giving some examples
Plugins provide specific tools for development. Libraries provide on API, the coder can use it to develop some features when writing code.Framework is a collection of libraries, tools, rules, structures, and control, to build software systems.
At development time in plugin (source code files, modules, packages, executables, etc.) is placed in the project, and apply some configurations using code,In libraries at the development time add the library to the project (source code files, modules, packages, executables, etc.) and call the necessary functions/methods using the given packages/module/classes, In Framework at the development time it create the structure of the application, place your code in necessary places,you may use the given libraries to write your code and you can include additional libraries and plugins.
At runtime the plug-in will be invoked via the configurations, At runtime the library will be called by the code and at runtime the framework will call your code (inverse of control).



Comments