Industry Practices and Tools 1
- hassamadhi9594
- Feb 19, 2019
- 9 min read
Updated: Feb 22, 2019
01).What is the need for VCS?
Version control systems(VCS) are a category of software tools that help a software team to manage changes to source code over time.
Version control software keeps track of every modification to the source in a special kind of database.
Version control is the ability to manage the change and configuration of an application. Versioning is a priceless process, especially when you have multiple developers working on a single application, because it allows them to easily share files. Without version control, developers will eventually step on each other’s toes and overwrite code changes that someone else may have completed without even realizing it. Using these systems allows you to check files out for modifications, then, during check-in, if the files have been changed by another user, you will be alerted and allowed to merge them.
Version control systems allow you to compare files, identify differences, and merge the changes if needed prior to committing any code. Versioning is also a great way to keep track of application builds by being able to identify which version is currently in development, QA, and production.
Another great use for versioning is when troubleshooting an issue, you are able to easily compare different versions of files to track differences.
02).Differentiate the three models of VCSs, stating their pros and cons
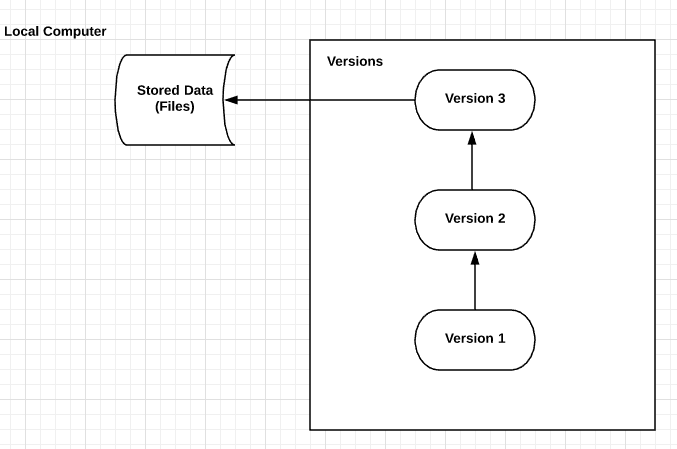
Local version control system
Local version control system maintains track of files within the local system. This approach is very common and simple. This type is also error prone which means the chances of accidentally writing to the wrong file is higher.
PROS : Oldest VCS.
Everything is in your Computer.
CONS : Cannot be used for
collaborative software development
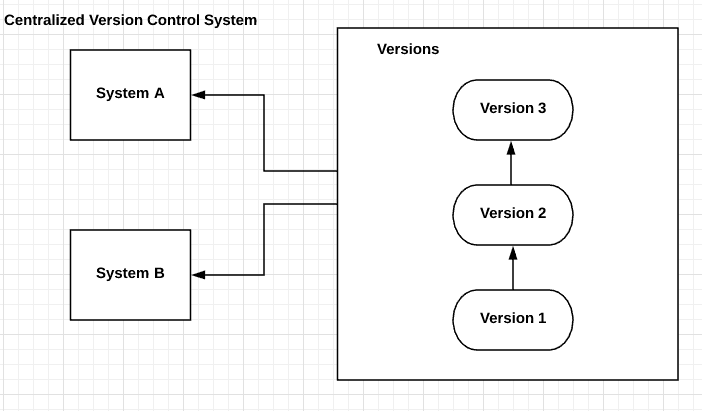
Centralized version control system
Centralized version control systems are based on the idea that there is a single “central” copy of your project somewhere (probably on a server), and programmers will “commit” their changes to this central copy.
PROS :Can be used for collaborative software development.
Everyone knows to a certain degree what others on the project are doing.
Administrators have fine grained control over who can do what.
CONS :Most obvious is the single point of failure that the centralized server represents.
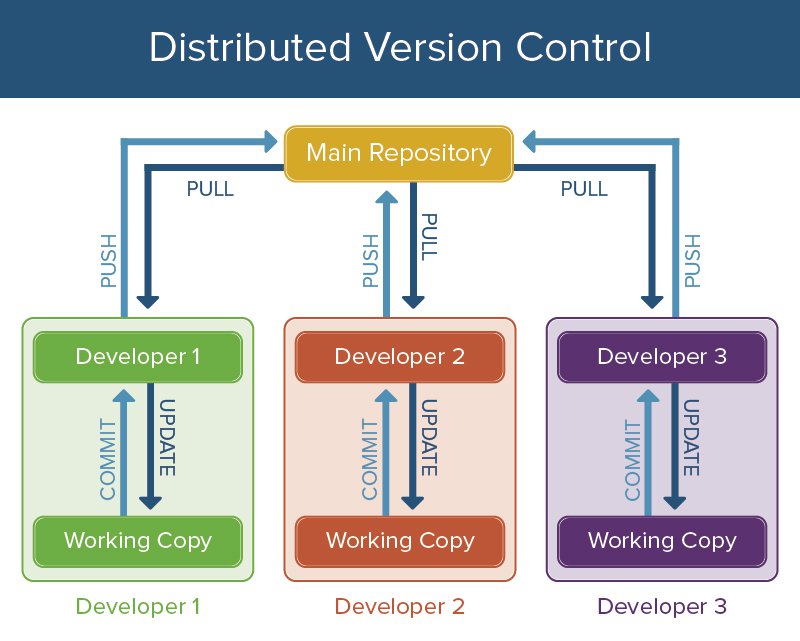
Distributed Version Control Systems
In software development, distributed version control (also known as distributed revision control) is a form of version control where the complete codebase - including its full history - is mirrored on every developer's computer.
PROS :No single point of failure.
Clients don’t just check out the latest snapshot of the files: they fully mirror the repository.
If any server dies, and these systems were collaborating via it, any of the client repositories can be copied back.
Can collaborate with different groups of people in different ways simultaneously within the same project.
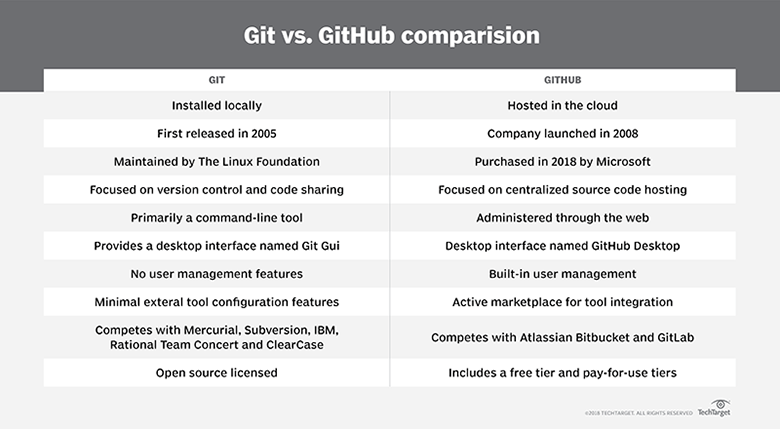
03).Git and GitHub, are they same or different? Discuss with facts
GIT is the most commonly used version control system today and has quickly become the
standard for version control. As a distributed revision control system it is aimed at speed, data integrity, and support for distributed, non-linear workflows. GIT was created by Linus Torvalds in 2005 for development of the Linux kernel.
Git is a distributed version control tool that can manage a development project's source code history, while GitHub is a cloud based platform built around the Git tool. Git is a tool a developer installs locally on their computer, while GitHub is an online service that stores code pushed to it from computers running the Git tool. The key difference between Git and GitHub is that Git is an open-source tool developers install locally to manage source code, while GitHub is an online service to which developers who use Git can connect and upload or download resources.
04).Compare and contrast the Git commands, commit and push
You can use programs with graphical user interfaces for Git. But you can also run terminal commands for Git. The terminal will be your paper on which you'll write Git commands. For the purpose of this article, we'll use the terminal (also called the command line) to run Git commands.
Git commit is the action of storing a new snapshot of the project’s state in the
VCS history. git commit. The "commit" command is used to save your changes to the local repository. ... Using the "git commit" command only saves a new commit object in the local Git repository. Exchanging commits has to be performed manually and explicitly (with the "gitfetch", "git pull", and "git push" commands).
The git push command is used to upload local repository content to a remote repository. Pushing is how you transfer commits from your local repository to a remote repo. ... Remote branches are configured using the git remote command. Pushing has the potential to overwrite changes, caution should be taken whenpushing.
05).Discuss the use of staging area and Git directory
Git doesn't have a dedicated staging directory where it puts some objects representing file changes (blobs). Instead, git has a file called the index that it uses to keep track of the file changes over the three areas: working directory, staging area, and repository. There are many uses of staging in git. Some are listed below:-
Staging helps you split up one large change into multiple commits.
Staging helps in reviewing changes.
Staging helps when a merge has conflicts.
Staging helps you keep extra local files hanging around.
Staging helps you sneak in small changes.
06).Explain the collaboration workflow of Git, with example
A Git Workflow is a recipe or recommendation for how to use Git to accomplish work in a consistent and productive manner. Git workflows encourage users to leverage Git effectively and consistently. Git offers a lot of flexibility in how users manage changes. Given Git's focus on flexibility, there is no standardized process on how to interact with Git. When working with a team on a Git managed project, it’s important to make sure the team is all in agreement on how the flow of changes will be applied. To ensure the team is on the same page, an agreed upon Git workflow should be developed or selected. There are several publicized Git workflows that may be a good fit for your team. Here, we’ll be discussing some of these workflow options.
In terms of Git process, collaboration is often about branching workflows. Thinking ahead on how you will intertwine commit trees will help you minimize integration bugs and support your release management strategy.
07).Discuss the benefits of CDNs
(CDN) is a geographically distributed network of proxy servers and their data centers. The goal is to provide high availability and high performance by distributing the service spatially relative to end-users. CDNs serve a large portion of the Internet content today, including web objects (text, graphics and scripts), downloadable objects (media files, software, documents), applications (e-commerce,
portals), live streaming media, on-demand streaming media, and social media sites.
Benifits of CDNs are :
Improving website load times - By distributing content closer to website visitors by using a nearby CDN server (among other optimizations), visitors experience faster page loading times.
As visitors are more inclined to click away from a slow-loading site, a CDN can reduce bounce rates and increase the amount of time that people spend on the site. In other words, a faster a website means more visitors will stay and stick around longer.
Increasing content availability and redundancy - Large amounts of traffic or hardware failures can interrupt normal website function. Thanks to their distributed nature, a CDN can handle more traffic and withstand hardware failure better than many origin servers.
Improving website security - A CDN may improve security by providing DDoS mitigation, improvements to security certificates, and other optimizations.
08).How CDNs differ from web hosting servers?
Web Hosting is used to host your website on a server and let users access it over the internet. A content delivery network is about speeding up the access/delivery of your website’s assets to those users.
Traditional web hosting would deliver 100% of your content to the user. If they are located across the world, the user still must wait for the data to be retrieved from where your web server is located. A CDN takes a majority of your static and dynamic content and serves it from across the globe, decreasing download times. Most times, the closer the CDN server is to the web visitor, the faster assets will load for them.
Web Hosting normally refers to one server. A content delivery network refers to a global network of edge servers which distributes your content from a multi-host environment.
09).Identify free and commercial CDNs
Content delivery networks (CDN) are the transparent backbone of the Internet in charge of content delivery. Whether we know it or not, every one of us interacts with CDNs on a daily basis; when reading articles on news sites, shopping online, watching YouTube videos or perusing social media feeds. Today, over half of all traffic is already being served by CDNs. Those numbers are rapidly trending upward with every passing year. The reality is that if any part of your business is online, there are few reasons not to use a CDN especially when so many offer their services free of charge. Yet even as a free service, CDNs aren’t for everyone. Specifically, if you are running a strictly localized website, with the vast majority of your users located in the same region as your hosting, having a CDN yields little benefit. In this scenario, using a CDN can actually worsen your website’s performance by introducing another unessential connection point between the visitor and an already nearby server.
10).Discuss the requirements for virtualization
System management is achieved using OS kernel functions executing in privileged CPU execution mode.
• To support one level of virtualization three distinct privilege levels of execution are required:
– Hypervisor
• Highest privilege
• Controls and manages all physical resources
– GuestOS
• De-privileged when compared to the hypervisor
• Controls and manages all virtual resources allocated to the specific VM
• Traps to Hypervisor kernel through hypervisor calls(?) for mapping and realizing virtual resource functions through physical resource access
– GuestUser
• Normal user mode privilege
• Traps to GuestOS kernel through system calls for virtual resource access
11).Discuss and compare the pros and cons of different virtualization techniques in different
levels
Here are the major pros and cons of virtualization.
Pros :
1. Reduced IT costs -
Virtualization helps businesses reduce costs in several ways, according to Mike Adams, senior director of cloud platform product marketing at VMware.
Capital expenditure savings. Virtualization lets companies reduce their IT costs by requiring fewer hardware servers and related resources to achieve the same level of computing performance, availability and scalability.
Operational expenditure savings. Once servers are virtualized, your IT staff can greatly reduce the ongoing administration and management of manual, time-consuming processes by automating operations, thus resulting in lower operational expenses.
Data center and energy-efficiency savings. As companies reduce the size of their hardware and server footprint, they lower their energy consumption, cooling power and data center square footage, thus resulting in lower costs.
2.Efficient resources utilization-
Virtualization enables businesses to get the most out of their investment in hardware and resources. "As customer data center environments grow in size and complexity, managing it becomes a burden," Adams said. "Virtualization can greatly help reduce this complexity by offering resource management capabilities to help increase efficiencies in these virtual environments."
Cons -
1.The upfront costs are hefty-
If you're transitioning a legacy system to a virtualized one, upfront costs are likely to be expensive. Be prepared to spend upwards of $10,000 for the servers and software licenses. However, as virtualization technology improves and becomes more commonplace, costs will go down D
2.Not all hardware or software can be virtualized-
12).Identify popular implementations and available tools for each level of visualization
There is a gap between development and implementation environments
•Different platforms
•Missing dependencies, frameworks/runtimes
•Wrong configurations
•Version mismatches
13).What is the hypervisor and what is the role of it?
A hypervisor or virtual machine monitor (VMM) is computer software, firmware or hardware that creates and runs virtual machine. A computer on which a hypervisor runs one or more virtual machines is called a host machine, and each virtual machine is called a guest machine. The hypervisor presents the guest operating systems with a virtual operating platfom and manages the execution of the guest operating systems.
14).How does the emulation is different from VMs?
Emulation and virtualization carry many similarities, yet they have distinct operational differences. If you’re looking to access an older operating system within a newer architecture, emulation would be your preferred route. Conversely, virtualized systems act independent of the underlying hardware.
Emulation can be effectively utilized in the following scenarios:
• Running an operating system meant for other hardware (e.g., Mac software on a PC; console-based games on a computer)
• Running software meant for another operating system (running Mac-specific software on a PC and vice versa)
• Running legacy software after comparable hardware become obsolete
Emulation is also useful when designing software for multiple systems. The coding can be done on a single machine, and the application can be run in emulations of multiple operating systems, all running simultaneously in their own windows.
While emulated environments require a software bridge to interact with the hardware, virtualization accesses hardware directly. However, despite being the overall faster option, virtualization is limited to running software that was already capable of running on the underlying hardware. The clearest benefits of virtualization include:
•Wide compatibility with existing x86 CPU architecture
•Ability to appear as physical devices to all hardware and software
•Self-contained in each instance
Between emulation and virtualization, your business can perform most virtual systems functions. While both services sound alike, it all revolves around how you utilize the software. If you want the software to get out of the way, virtualization allows guest code to run directly on the CPU. Conversely, emulators will run the guest code themselves, saving the CPU for other tasks.
15).Compare and contrast the VMs and containers/dockers, indicating their advantages and
disadvantages
Both containers and VMs have benefits and drawbacks, and the ultimate decision will depend on your specific needs, but there are some general rules of thumb.
VMs are a better choice for running apps that require all of the operating system’s resources and functionality, when you need to run multiple applications on servers, or have a wide variety of operating systems to manage.
Containers are a better choice when your biggest priority is maximizing the number of applications running on a minimal number of servers.
VMs Containers
Heavyweight Lightweight
Limited performance Native performance
Each VM runs in its own OS All containers share the host OS
Hardware-level virtualization OS virtualization
Startup time in minutes Startup time in milliseconds
Allocates required memory Requires less memory space
Fully isolated and hence more secure Process-level isolation, possibly less secure






Comments