Industry practices and tools 2
- hassamadhi9594
- Feb 25, 2019
- 5 min read
Updated: Mar 1, 2019
01).Discuss the importance of maintaining the quality of the code, explaining the different
aspects of the code quality
The quality of the code can be measured by different aspects
•Weighted Micro Function Points
• Halstead Complexity Measures
• Cyclomatic Complexity
• Lines of code
• Lines of code per method
• Etc…
02).Explain different approaches and measurements used to measure the quality of code
• Documenting the code. Comments improves the readability and the understandability of the code.
• Regular Code Reviews. According to a recent survey, software professionals rank code reviews as the number one way to improve programming. These reviews enable developers to collaborate and share
knowledge with each other, which improves their work. Furthermore, reviews ensure that code adheres to established standards.
• Functional Testing. Functional testing is important because it encourages developers to focus on
software functionality from the outset, reducing extraneous code. The aim of software development is to write an application that delivers exactly what users need.
• Clear Requirements. Most software development projects begin with a requirements document, or story cards in agile development. A project with clear, feasible requirements is much more likely to achieve high quality than ambiguous, poorly specified requirements.
03).Identify and compare some available tools to maintain the code quality
sonarqube
CSS LINT
Sidekick
sonarsourse
klocwork
w3c
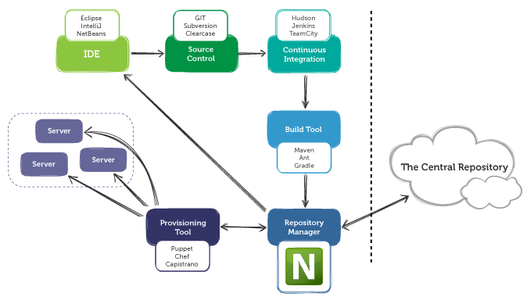
04).Discuss the need for dependency/package management tools in software development?
Software project may have a backbone framework and many external artefacts linked
•Third party packages
•External libraries
•Plug-ins
•Etc.
05).Explain the role of dependency/package management tools in software development
tools are manage external artefacts towards minimizing integration issues
06).Compare and contrast different dependency/package management tools used in industry
•Composer [php]
•Maven [Java]
•NuGet [.net]
•NPM (Node Package Manager) [JS]
•Bower [JS]
07).What is a build tool? Indicate the significance of using a build tool in large scale software
development, distinguishing it from small scale software development
Build tools are programs that automate the creation of executable applications from source code. Building incorporates compiling, linking and packaging the code into a usable or executable form. In small projects, developers will often manually invoke the build process. This is not practical for larger projects, where it is very hard to keep track of what needs to be built, in what sequence and what dependencies there are in the building process. Using an automation tool allows the build process to be more consistent.
In small projects, developers will often manually invoke the build process. This is not practical for larger projects, where it is very hard to keep track of what needs to be built, in what sequence and what dependencies there are in the building process. Using an automation tool allows the build process to be more consistent.
08).Explain the role of build automation in build tools indicating the need for build automation
•A necessary pre-condition for continuous integration and continuous testing
•Accelerate the compile and link processing
•Eliminate redundant tasks
•Minimize "bad builds"
•Documentation – has the history of builds and releases in order to investigate issues
•Save time and money, and improve product quality
09).Compare and contrast different build tools used in industry
•Ant/Ivy
•Maven
•Gradle
•Sbt
•MSBuild
10).Explain the build life cycle, using an example (java, .net, etc…)
Maven is based around the central concept of a build lifecycle. What this means is that the process for building and distributing a particular artifact (project) is clearly defined.
For the person building a project, this means that it is only necessary to learn a small set of commands to build any Maven project, and the POM will ensure they get the results they desired.
There are three built-in build lifecycles: default, clean and site. The default lifecycle handles your project deployment, the clean lifecycle handles project cleaning, while the site lifecycle handles the creation of your project's site documentation.
11).What is Maven, a dependency/package management tool or a build tool or something
more?
Maven uses Convention over Configuration, which means developers are not required to create build process themselves. Developers do not have to mention each and every configuration detail. Maven provides sensible default behavior for projects.
Make the build process easy — The programmers doesn’t need to know much about the process of how maven works or provide every configuration settings manually
Provide a uniform build system — Working on a one project with maven is sufficient to work on other maven projects
Provide quality project information — Maven provides user to specify the project information using the POM and make them available to use whenever needed. Some information are generated from the source of the project
Provide guidelines for development best practicesAllowing transparent migration to new features — Provide the ability to take advantage of updated versions of the dependencies and plugins for the same project (programmer can use updated or newly added Plugins)
12).Discuss how Maven uses conventions over configurations, explaining Maven’s approach to
manage the configurations
Maven uses Convention over Configuration, which means developers are not required to create build process themselves. Developers do not have to mention each and every configuration detail. Maven provides sensible default behavior for projects.
13).Discuss the terms build phases, build life cycle, build profile, and build goal in Maven
~Apache Maven 2.0 goes to great lengths to ensure that builds are portable. Among other things, this means allowing build configuration inside the POM, avoiding all filesystem references (in inheritance, dependencies, and other places), and leaning much more heavily on the local repository to store the metadata needed to make this possible.
However, sometimes portability is not entirely possible. Under certain conditions, plugins may need to be configured with local filesystem paths. Under other circumstances, a slightly different dependency set will be required, and the project's artifact name may need to be adjusted slightly. And at still other times, you may even need to include a whole plugin in the build lifecycle depending on the detected build environment.
A Build profile is a set of configuration values, which can be used to set or override default values of Maven build. Using a build profile, you can customize build for different environments such as Production and Development environments.When we execute mvn post-clean command, Maven invokes the clean lifecycle consisting of the following phases.
•pre-clean
• clean
•post-clean
•Maven clean goal (clean:clean) is bound to the clean phase in the clean lifecycle
•Its clean:cleangoal deletes the output of a build by deleting the build directory
~Maven is based around the central concept of a build lifecycle. What this means is that the process for building and distributing a particular artifact (project) is clearly defined.
For the person building a project, this means that it is only necessary to learn a small set of commands to build any Maven project, and the POM will ensure they get the results they desired.
There are three built-in build lifecycles: default, clean and site. The default lifecycle handles your project deployment, the clean lifecycle handles project cleaning, while the site lifecycle handles the creation of your project's site documentation.
~A plugin goal represents a specific task (finer than a build phase) which contributes to the building and managing of a project. It may be bound to zero or more build phases. A goal not bound to any build phase could be executed outside of the build lifecycle by direct invocation.
~
14).Discuss with examples, how Maven manages dependency/packages and build life cycle
A Build Lifecycle is a well-defined sequence of phases, which define the order in which the goals
are to be executed. The primary(default) life cycle of Maven is used to build the application, using 23 phases
• Validate
• Initialize
• Generate-sources
• Compile
• Generate-test-sources
• Etc.
15).Identify and discuss some other contemporary tools and practices widely used in the
software industry
•Continuous Integration
•Configuration Management
•Test automation
•Issue/bug tracking tools
•Agile methodologies, DevOps



Comments